Exploring Mathematical Research-Data Management
Interested in the world of mathematical research-data management but not sure where to start? Explore the basics with this collection of resources (originally published in our newsletter)
What kind of data exists in mathematical research? Is there data at all, or does this appear only in other sciences? Read on and follow our exploration of mathematical research data, and the special role of mathematics in the sciences as reflected in this new data culture. We use the term 'Mathematical Research Data' to describe a wide range of objects generated through mathematical research. This information can take the form of raw experimental data, theoretical models, computational outputs or... In order to gain an understanding of the nature of this data landscape, we recommended that you explore our newletter article "Research Data in Math".
How (on earth) do I properly handle my research data? Wait, what do I put in a Research Data Management Plan? If you’ve been wondering, then we’ve got you covered! In this article, we will walk you through a few key points to consider for proper data management, and offer examples and tools.
Pen and paper, chalk and blackboard, a big cup of coffee... What else does a mathematician need? In this article, we will follow the evolution of scientific tools that have changed the practice of mathematics research.
"I read articles and books, discuss with collaborators, think about a problem, and eventually, write and publish papers. I use no data!” Read our fictional (but realistic) questions and answers regarding the topic of “I have no data”.
FAIR Mathematics
What are the FAIR principles and how can they be applied in maths?
In the near-infinite resource aka World Wide Web, where do you find your research data? Where are the concentrating resource “hubs”? How is MaRDI proposing to help with the Findability challenges?
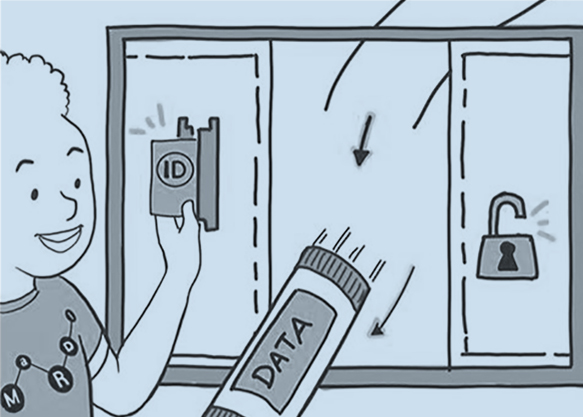
The A in FAIR stands for Accessibility. This means using modern standards and protocols to identify, gain access and retrieve data; but also making sure that all research data supporting a result is available, enabling verifiability and applicability. Beyond that, there is a whole philosophical debate on open-access, the right to information, and the standard practices of the research community.
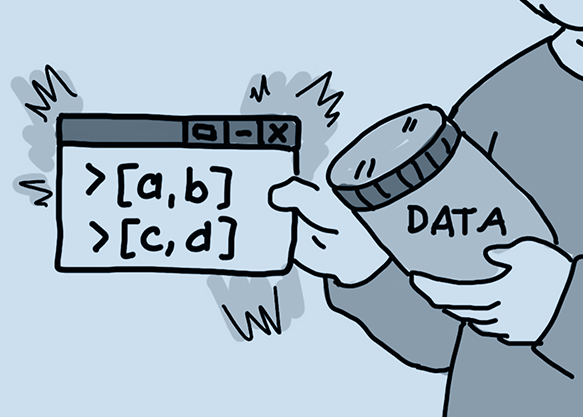
Interoperability is compatibility, community, and working together. This article provides a panoramic view of the efforts made by MaRDI to bring researchers together and set the future of sharing mathematical research data.
While Findablity, Accessiblity, and Interoperablity are necessary conditions for effective reuse of research data, Reusability is the ultimate goal of the FAIR principles. Read about the challenges regarding documentation, verifiability, as well as legal barriers, and community standards.
Modern Mathematics
A collection of articles revolving around modern mathematics.
We will discuss what are knowledge graphs in general and their role in structuring mathematical knowledge. On top of that, we will speculate about the future of knowledge graphs and artificial intelligence.
The four-color theorem was the first major theorem in pure mathematics whose proof absolutely required the assistance of a computer. The story of its development, reactions, and impact is paradigmatic of how and why a research data perspective became relevant and necessary in modern mathematics.
Our Newsletter "Math & Data Quarterly" is prepared by our partner IMAGINARY. Sign up to get it delivered straight to your inbox quarterly or check it out online.